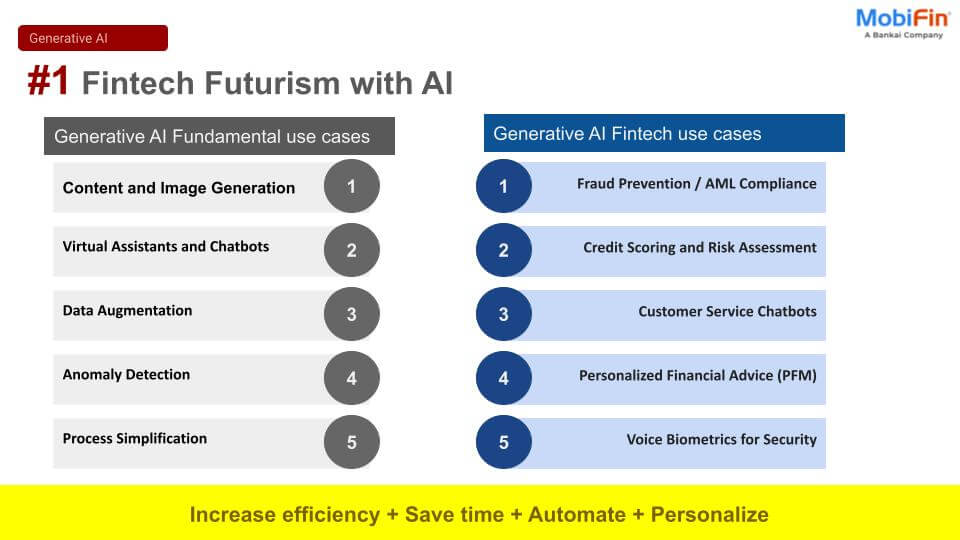
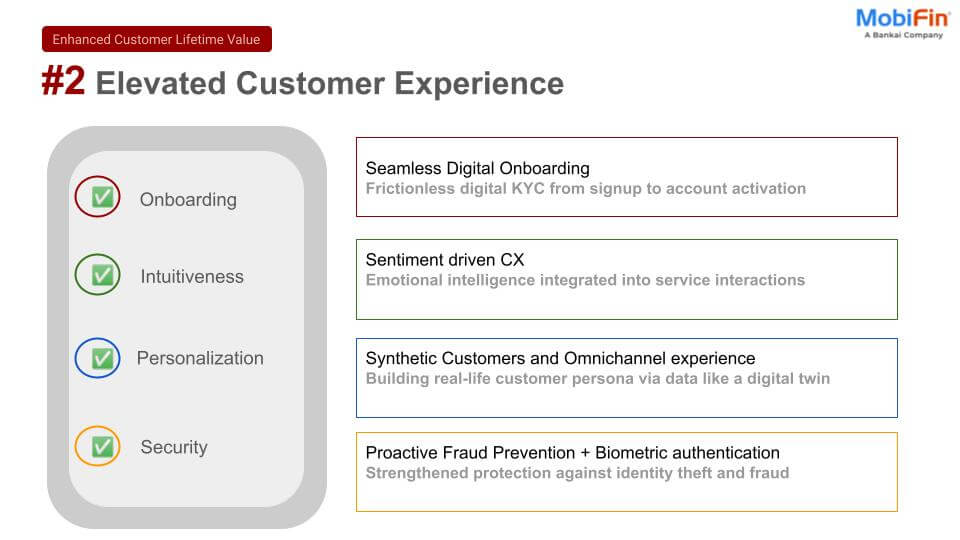
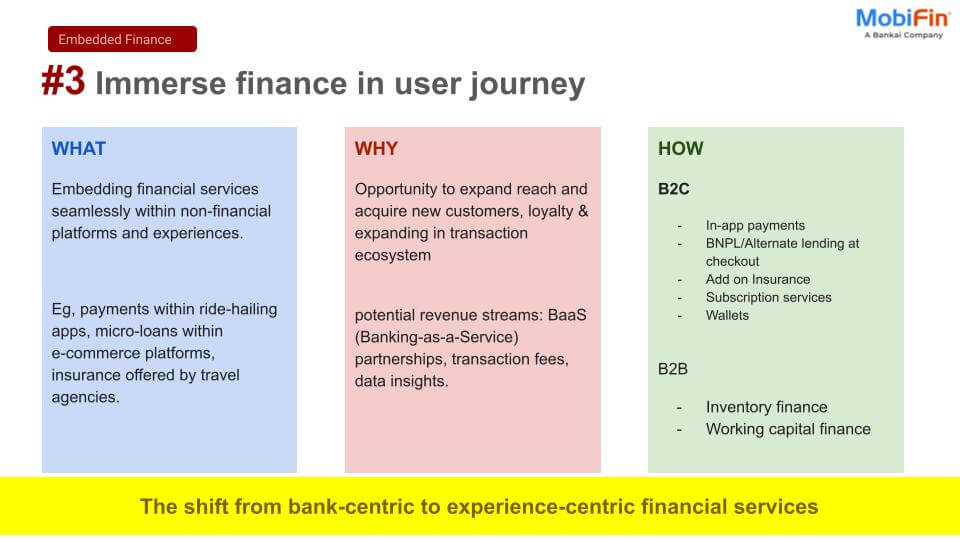
We are seeing firsthand how businesses are innovating and enhancing digital payment solutions, enabling frictionless financial services for their customers. But what exactly makes embedded finance such a game-changer?
Embedded finance is reshaping the world of money by integrating financial services directly into non-financial platforms. From seamless payment options within shopping apps to embedded lending and insurance, it redefines customer convenience and accessibility.
The global embedded finance market, valued at USD 82.48 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to USD 1,029.02 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 32.4% from 2024 to 2032. Such a level of growth reflects embedded finance’s significance in transforming how consumers interact with financial services across industries.
The shift toward embedded finance
The shift toward embedded finance reflects a fundamental change in how financial services are delivered and consumed. Consumers now demand increased convenience, expecting seamless access to payments, credit, and insurance within their favorite apps.
By integrating financial services directly into these ecosystems, businesses are meeting modern expectations while opening new avenues for innovation and customer retention.
• Consumer expectations – Today’s consumers expect financial services to be as accessible and integrated as possible. They want to manage payments, access credit, or buy insurance without leaving their favorite apps. Embedded finance helps meet these expectations by delivering these services at the exact point of need.
• Digital-first ecosystem – The rise of ecommerce and digital services has set the stage for embedded finance, driven by the increased use of mobile devices. This shift is especially prominent in regions with high mobile penetration rates, where embedded finance services are often the chosen mode of financial interaction.
Key use cases for embedded finance
Embedded finance unlocks diverse use cases that enhance both customer convenience and business growth. From Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services that offer flexible payment options to embedded payments that streamline in-app transactions, the possibilities are vast. These use cases demonstrate the power of embedding financial services directly into everyday platforms.
• Buy now pay later (BNPL) – BNPL services have skyrocketed in popularity, especially among younger consumers who value flexible payment options. The global BNPL market was valued at USD 30.38 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 37.19 billion in 2024 to USD 167.58 billion by 2032.
• Embedded payments – Companies use embedded payment systems that enable users to make in-app payments without switching platforms, increasing transaction ease and completion rates.
• Lending as a feature – Platforms offering embedded lending provide users with immediate access to funds, making credit accessible to those who may not have traditional banking relationships. This feature has been particularly beneficial for small businesses needing quick funding.
• Insurance and wealth management – Embedded finance allows companies to offer microinsurance and investment options at the point of sale, helping consumers manage risks and investments more efficiently.
The benefits of embedded finance for businesses
Embedded finance empowers businesses with enhanced customer loyalty by seamlessly integrating financial services into their platforms, keeping users captively engaged. It unlocks new revenue streams, such as fees from embedded payments or interest from lending.
Additionally, it provides actionable insights through data-driven innovation, enabling companies to offer personalized and relevant services. This strategic integration not only boosts customer satisfaction but also drives long-term growth.
• Increased customer retention – With embedded finance, companies can deliver financial services directly in-platform, keeping customers engaged and loyal by meeting their needs where they already are.
• New revenue streams – Embedded finance allows companies to generate additional income through services like payment processing fees, interest on loans, or insurance premiums.
• Data-driven innovation – Embedded finance generates valuable data on customer spending, lending habits, and risk tolerance. Companies can leverage this data to refine services and offer more personalized experiences.
The benefits of embedded finance for customers
Embedded finance offers numerous benefits for customers, improving their financial experience and accessibility. Customers can access services like payments, lending, and insurance within the platforms they are already using, reducing friction and creating a unified experience.
• Reduced financial barriers – Embedded finance democratizes access to financial services, especially for underserved populations. By bringing services like microloans and microinsurance to mobile apps and digital platforms, embedded finance enables greater financial inclusion, allowing more people to access essential services regardless of traditional banking access.
• Personalization and relevance – Through data insights, embedded finance providers can offer personalized financial products tailored to customer needs and preferences. For instance, insurance providers can suggest coverage options based on purchasing behavior, while digital wallets can recommend savings plans based on spending habits.
• Improved financial literacy – Embedded finance also has the potential to improve financial literacy. By placing these services within widely used platforms, companies can offer education on budgeting, credit, and investment at the point of need.
The role of fintech enablers
Fintech enablers are at the core of driving the embedded finance revolution, bridging the gap between financial services and everyday platforms. These innovators not only enhance user convenience but also unlock opportunities for businesses to drive growth by delivering tailored, data-driven financial solutions.
• Facilitating embedded finance – Fintech enablers play a pivotal role in making embedded finance accessible, especially in emerging markets. By integrating financial services into non-banking platforms, fintech providers help bridge the gap in underserved areas.
• Innovative payment solutions – Fintech companies have led the way in creating digital wallets and instant payment options, making transactions smoother and safer for consumers.
• API and partnership models – APIs are essential for embedded finance, as they enable seamless integration of financial services into non-banking platforms. These partnerships allow both fintech and non-financial companies to collaborate on delivering services.
Challenges and considerations for embedded finance
While embedded finance is revolutionizing the financial landscape, it comes with its own set of challenges. Building transparency and trust remains essential for ensuring customers feel confident in the reliability and security of embedded financial services.
• Regulatory compliance – Regulatory landscapes vary significantly, and compliance can be challenging, particularly in cross-border contexts. Adhering to local laws is crucial to ensuring customer safety and service reliability.
• Security concerns – Embedded finance increases the volume of sensitive financial data on digital platforms, which heightens the importance of secure systems. Data breaches can erode customer trust and harm a company’s reputation.
• Customer trust – For embedded finance to succeed, companies must prioritize transparency and build customer trust. Consumers need to feel confident that their data is secure and that the services they are accessing are reliable.
The future of embedded finance
The future of embedded finance is poised to extend far beyond simple payment solutions, evolving into comprehensive services such as AI-powered investment management, tailored budgeting tools, and personalized lending options. As smartphones become more accessible in emerging markets, embedded finance holds the promise of driving widespread financial inclusion.
With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, the next wave of embedded finance will offer even more predictive and customized experiences, seamlessly integrating financial services into every facet of consumers’ digital interactions
• Beyond payments – The future of embedded finance goes beyond payments to include services like investment management, budgeting tools, and even full-service banking integrated into consumer apps.
• Global adoption – Emerging markets represent a significant opportunity for embedded finance, with a high demand for accessible financial solutions. As smartphone adoption increases globally, embedded finance is likely to become the norm in these regions.
• The role of AI – AI will enhance embedded finance by providing tailored, predictive insights for users. Through AI, platforms can anticipate consumer needs, such as offering personalized loan recommendations or investment options.
Conclusion
Embedded finance is rapidly changing the way businesses and consumers interact with financial services. By integrating these services at the right place and time, companies can offer enhanced convenience, foster financial inclusion, and unlock new revenue streams. The future of embedded finance promises continued innovation, from AI-driven personalization to expanded offerings in emerging markets.
As we navigate an era of unparalleled digital transformation, MobiFin stands at the forefront of redefining financial possibilities. By combining visionary technologies with a deep understanding of market needs, MobiFin is committed to shaping a future where financial services seamlessly integrate into the fabric of everyday life, benefitting businesses and individuals alike.
Ready to revolutionize the way you engage with financial services? Partner with MobiFin to leverage innovative solutions that bring seamless, secure, and future-forward experiences that will drive your growth.
Connect with us to know how we can shape the future of finance together.